In an era increasingly defined by artificial intelligence, a silent but profound crisis is brewing at the heart of our digital world: the escalating strain on global data centers. The rise of Generative AI (Gen AI) – models capable of creating new content, from text and images to code and music – has ushered in an unprecedented demand for computational power. This insatiable appetite is pushing our existing data center infrastructure to its limits, creating a multifaceted crisis characterized by soaring energy consumption, physical space limitations, and complex supply chain challenges.
Data centers, the unseen engines of the internet, are the physical homes for the servers, storage, and networking equipment that power our digital lives. They are the backbone of cloud computing, streaming services, and, increasingly, the complex algorithms that drive AI. However, the sheer scale and intensity of Gen AI workloads are transforming these critical facilities into energy behemoths, consuming vast amounts of electricity and generating immense heat. This rapid expansion, coupled with the need for sustainable and efficient operations, presents a formidable challenge that demands immediate and innovative solutions.
This article will delve into the core drivers of this emerging data center crisis, examining why Gen AI is so power-hungry and the subsequent impacts on our energy grids, environment, and economic landscape. More importantly, we will explore the cutting-edge solutions and strategic shifts required to power the future of AI responsibly and sustainably. From next-generation cooling technologies and energy-efficient hardware to novel data center designs and renewable energy integration, we will uncover the path forward in addressing this critical infrastructure challenge. The future of AI, and indeed our digital future, hinges on our ability to build a robust, resilient, and sustainable data center ecosystem.
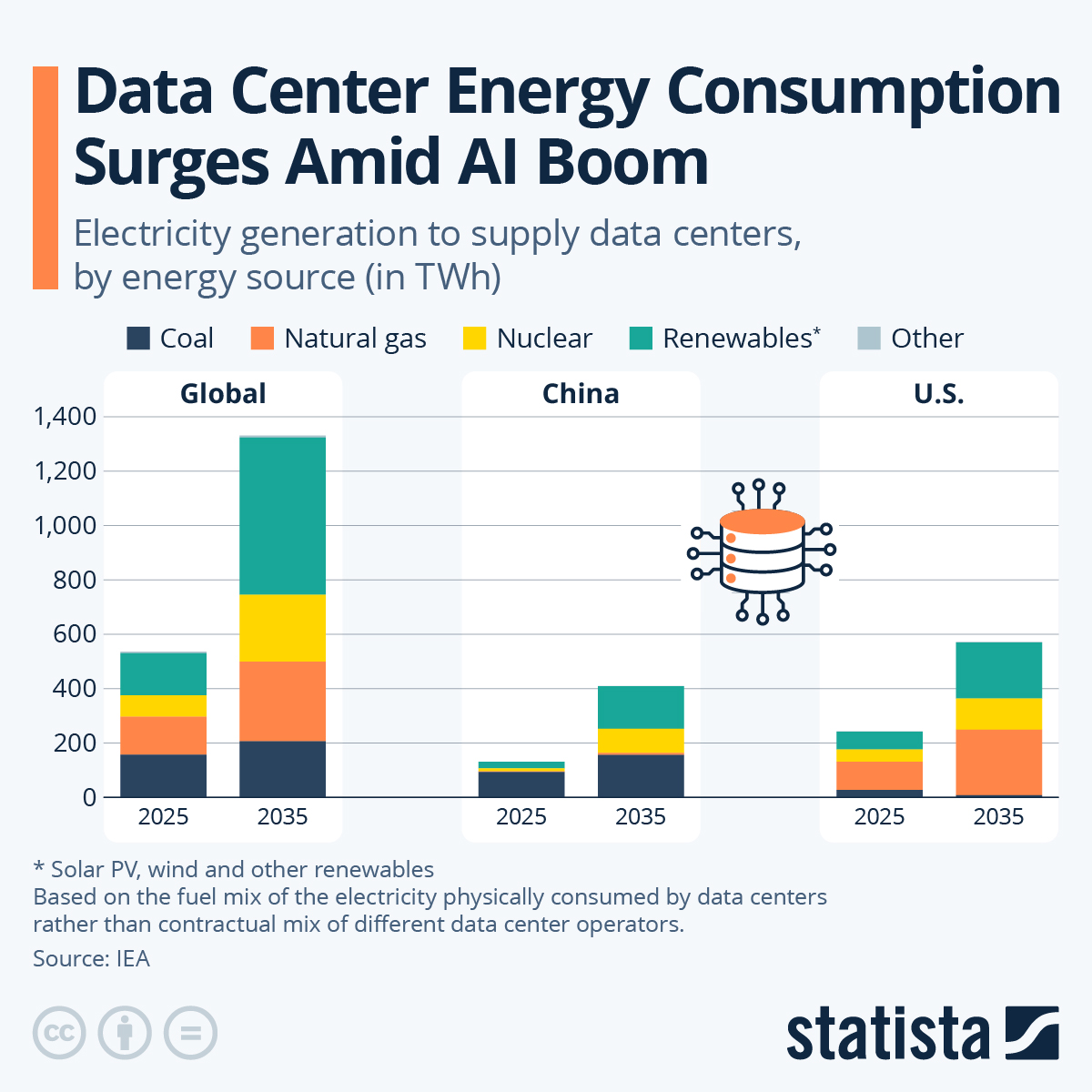
The Drivers of the Data Center Crisis
The data center crisis is driven by several converging factors, significantly amplified by Generative AI:
The Gen AI Power Surge
Generative AI models are computationally intensive. Training involves feeding massive datasets to billions of parameters, running on thousands of high-performance GPUs, consuming immense power. Inference, while less intensive, will also skyrocket as Gen AI applications become widespread.
Exponential Data Growth
Unprecedented data generation from every digital interaction fuels the need for more data center capacity. Gen AI exacerbates this, requiring even larger datasets, creating a feedback loop of data generation and consumption.
Physical Constraints and Location Challenges
Building data centers is complex, requiring vast land, robust power grids, and access to cooling resources. Suitable locations are scarce and expensive, and connecting to grids requires costly upgrades. Water-intensive cooling systems also pose challenges in water-scarce regions.
Supply Chain Bottlenecks
Specialized hardware for AI workloads faces high demand and supply chain constraints. Shortages of GPUs, AI accelerators, and cooling systems delay data center expansion, hindering capacity to meet demand.
The Cooling Conundrum
AI hardware generates immense heat. Efficiently removing this heat is paramount. Traditional air-cooling is becoming ineffective for high-density AI racks, necessitating advanced and sustainable cooling solutions.

The Multifaceted Impacts of the Crisis
The data center crisis impacts energy systems, economies, and technological innovation:
Energy Consumption and Environmental Strain
Increased electricity consumption from data centers strains power grids, potentially leading to instability and blackouts. Reliance on fossil fuels contributes to carbon emissions, and water-intensive cooling exacerbates water scarcity.
Economic Consequences
Rising costs of building and operating data centers lead to higher cloud service and AI infrastructure costs. Governments face massive investment burdens for grid upgrades. The high cost of AI infrastructure could also create a digital divide.
Innovation Bottleneck
If data center capacity cannot keep pace, it could slow AI research and hinder deployment of AI applications at scale. High barriers to entry could also stifle competition.
Geopolitical Tensions
AI's strategic importance fuels geopolitical competition for resources like semiconductors and clean energy. Supply chain vulnerabilities and data sovereignty concerns further complicate the global data center landscape.
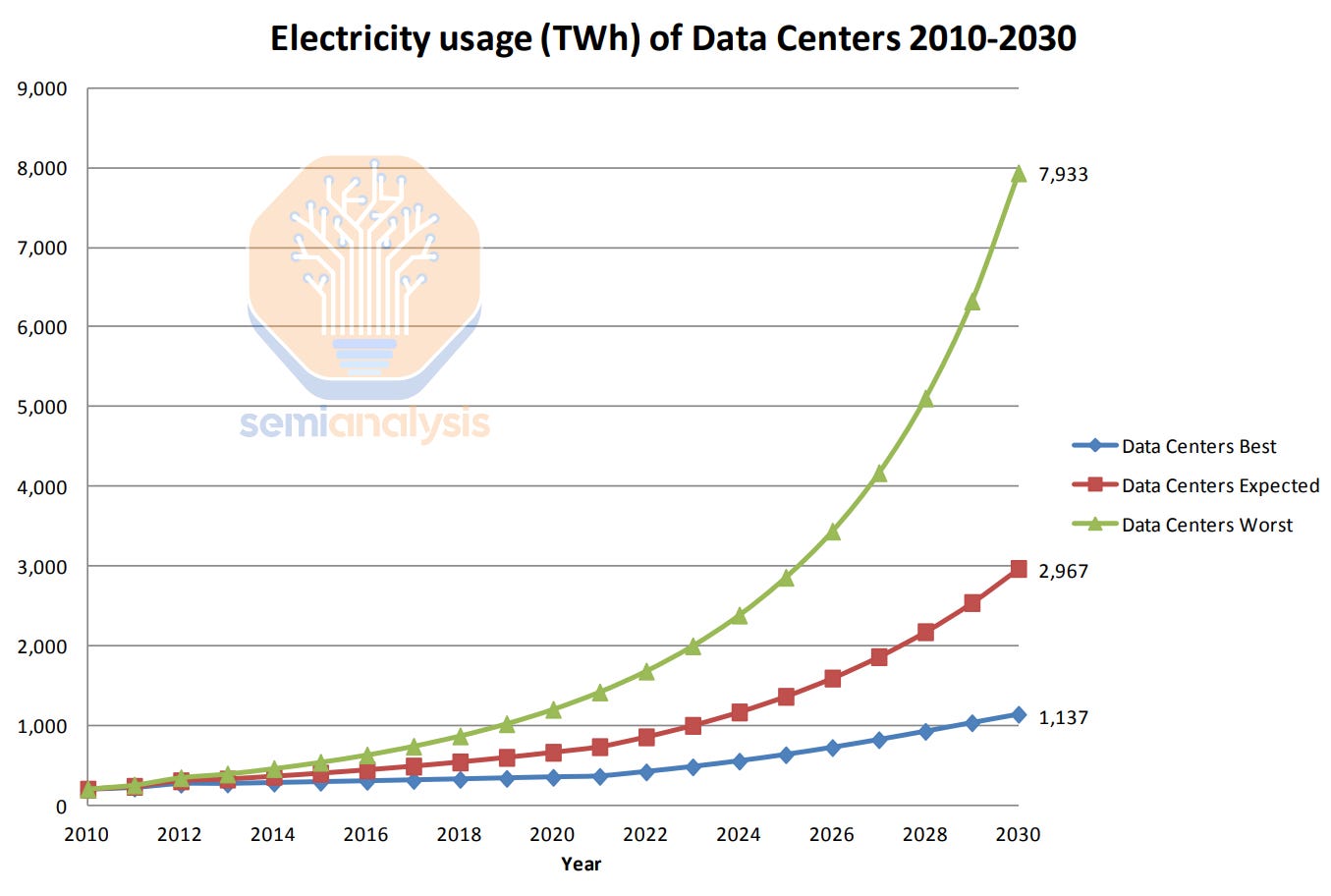
Innovative Solutions and the Path Forward
Addressing the data center crisis requires technological innovation, strategic planning, and sustainability:
Sustainable Power Sources
Transitioning to renewable energy (solar, wind, geothermal) is critical. Advanced energy technologies like small modular reactors (SMRs) and smart grids are also vital for managing fluctuating renewable sources.
Next-Generation Cooling Technologies
Liquid cooling (direct-to-chip and immersion) offers superior heat transfer and energy efficiency. Geothermal cooling also reduces reliance on mechanical systems.
AI for AI: Optimizing Data Center Operations
AI-powered management systems can optimize cooling, manage power distribution, and predict maintenance needs, minimizing energy waste and maximizing efficiency.
Hardware Innovation
Developing energy-efficient chips and specialized hardware like AI accelerators, neuromorphic computing, and optical computing can significantly reduce power consumption.
Data Center Design and Location Strategy
Rethinking data center design (modular, underwater) and strategic siting in regions with abundant renewable energy and cooler climates are crucial.
Software and Algorithmic Efficiency
Optimizing AI models and algorithms through techniques like quantization and pruning, and ensuring efficient software stacks, can yield significant energy savings.

Case Studies and Industry Initiatives
The data center crisis has spurred significant investment and innovation:
•Hyperscalers Leading the Way: Google aims for 24/7 carbon-free energy by 2030 and uses AI to optimize cooling [1]. Microsoft explores underwater data centers and liquid cooling [2]. AWS invests heavily in renewable energy.
•Liquid Cooling Adoption: Companies like GRC and Submer specialize in immersion cooling solutions for high-density AI racks.
•Chip Design for Efficiency: NVIDIA continuously improves the energy efficiency of its GPUs.
•Government and Industry Collaboration: Governments implement policies for sustainable practices, and industry consortiums promote best practices and research.
Conclusion
The data center crisis, driven by Gen AI, is a formidable challenge but also an opportunity to rethink digital infrastructure. Addressing it requires collaborative efforts in renewable energy, next-generation cooling, energy-efficient hardware and software, and innovative data center designs. By acting decisively, we can power a future where AI thrives responsibly and sustainably.





